GitHub Actions Cheat Sheet
Overview
GitHub Actions is a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) platform that enables automated build, test and deployment pipelines. GitHub Actions also enables the execution of non-CI/CD type automation on a repository, like adding a label when someone creates a new issue on the repository.
GitHub Actions supports Linux, Windows and macOS operating systems

Event(s)
A specific activity in a repository that triggers a workflow execution
Examples:
- A user creates a
pull request - A user opens an
issue - A user pushes a
committo a repository - Other example events that trigger workflows

[skip ci] or [ci skip] in the commit message. GitHub recognizes this phrase and will not trigger the CI workflow for that commit.Workflow(s)

A configurable automated process:
- Made up of one or more jobs defined by a YAML associated to a repository
- Found in
.github/workflows - A given repo can have multiple workflows
- Runs when:
- Triggered by an event in a repository
- Triggered manually
- Triggered via another workflow (workflows can reference other workflows)
- Posting to a REST API
- Per a defined schedule
Examples:
- A workflow to build and test pull requests
- A workflow to deploy your application every time a release is created
- A workflow to add a label every time someone opens a new issue
Runner(s)
- A server that runs your workflows when they are triggered
- A given runner can execute a single job at a time
- Ubuntu Linux, Windows and macOS provided (hosted) by GitHub
- Each workflow runs on a fresh,
newly-provisionedvirtual machine - Runners come in different configurations to meet specific needs
- Users can leverage GitHub hosted or self-hosted runners
Job(s)
A set of steps in a workflow that execute on the same runner
Each job runs within a virtual machine (runner) OR container
Jobs run in parallel by default but can be configured to depend upon one another using
needskeywordEach job contains one or more step(s)
Steps can be a shell command
[run]or an action[uses]Runs when:
- Invoked within a workflow
- When the prior / dependent job within the workflow finishes
- Simultaneously with another job within the workflow
- In the context of a matrix
Examples:
- Separate, unique build jobs for different architectures
- A packaging job
- A deployment job
jobs: job_1: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - run: echo "The job was triggered by a ${{ github.event_name }} event." - run: echo "The drive is '${{ github.event.inputs.homedrive }}'." - run: echo "The environment is '${{ github.event.inputs.environment }}'." - run: echo "The log level is '${{ github.event.inputs.logLevel }}'." - run: echo "Should run the matrix? '${{ github.event.inputs.run_matrix }}'." job_2: runs-on: ubuntu-latest needs: job_1 steps: - run: echo "Status ${{ job.status }}" job_3: runs-on: ubuntu-latest needs: job_1 steps: - run: echo "Services ${{ job.services }}" job_4: runs-on: ubuntu-latest needs: [job_2, job_3] steps: - run: echo "Status ${{ job.status }}" - name: Step Summary run: echo "All the jobs completed in ${{ github.ref }} branch!" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
You can set some custom Markdown for each job summary to display and group unique content, such as test result summaries, failures and so on. GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY is an unique environment variable for each step in a job.
echo "{markdown content}" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
Step(s)
Granular execution of a job
Steps can be a shell command (
run) or an action (uses)Data can be shared from one step to another
When using the
runcommand it runs in the same process/same directory in ashellBy default, GitHub Actions uses
bashon Linux andpwshon Windows. If you want to specify a different shell, you need to use theshellkeyword.The availability of some shells may depend on the runner environment (e.g., Ubuntu, Windows, MacOS). Always ensure that the shell you are trying to use is available in your runner’s environment.
Runs when:
- Invoked within a job
- When the prior step finishes
Examples:
- A step that builds your application
- A step that pushes an artifact to the artifact repository

Action(s)
A reusable step is an Action
Reduces the amount of repetitive code written in Workflow files
Actions can be self-created / customized, or provisioned from the GitHub Marketplace.
Lives in a independent public repository.
Can be written in JavaScript/Typescript(
NodeJS).May use GitHub Actions Toolkit for command line argument parsing, passing parameters, interacting with the GitHub API.
The most minimal action definition is composed of a
nameand arunsobject to define how the action is executed and what file to run.name: "HelloWorld Action" description: "Says Hello!" author: "Avijit Chatterjee" runs: using: "node20" main: "dist/index.js" branding: icon: "aperture" color: "green"
Could be written as a
Dockercontainer that does the the action logic and reference it from the registry like say Docker Hub when invoking the action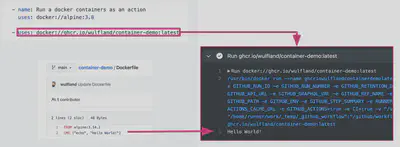
Could be a
CompositeAction where you would basically combine multiplerunandusescommand steps into a single action.- Here’s a simple example of a composite GitHub action that runs a set of commands to set up a
Node.jsenvironment, install dependencies, and run tests.name: 'Setup Node.js' description: 'Sets up a Node.js environment, installs dependencies, and runs tests' inputs: node-version: description: 'Node.js version to use' required: true default: '14' working-directory: description: 'The directory to run commands in' required: false default: '.' outputs: test-results: description: 'The result of the test run' runs: using: "composite" steps: - name: Set up Node.js uses: actions/setup-node@v3 with: node-version: ${{ inputs.node-version }} - name: Install Dependencies run: npm install working-directory: ${{ inputs.working-directory }} - name: Run Tests run: npm test working-directory: ${{ inputs.working-directory }} continue-on-error: true id: tests - name: Set Output for Tests run: echo "test-results=${{ steps.tests.outcome }}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- Here’s a simple example of a composite GitHub action that runs a set of commands to set up a
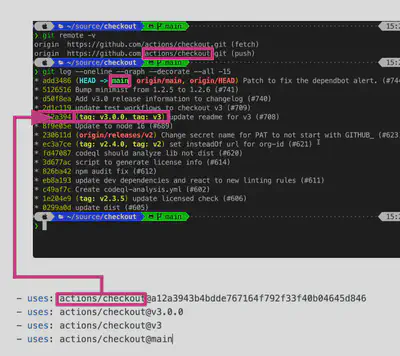
Whichever way you create it the
Actiondefinition is stored in theaction.ymlfile, put directly in the root of the repository.Use
Semanticversioning to build and maintain your Actions. When you or others refer/use your Action you would do so like:- {owner}/{repo}@{ref}
- {owner}/{repo}/{path}@{ref}
- where ref could be SHA / Tag / Branch
Pass variables to Action
with: The
withkeyword allows you to specify inputs for actions. These inputs can be defined in the action.yml file and can have default values, data types, and descriptions. This method is typically used for passing configurable parameters that the action will use.env: The
envkeyword is used to set environment variables that can be accessed in the action. Environment variables are global within the job and can be useful for passing sensitive data (e.g., secrets) or shared configurations.
Examples:
- Pull a given git repository for GitHub
- Set up the correct toolchain for a build environment
- Establish authentication to a cloud provider
Context
Every workflow execution has access to different Context information during runtime. Contexts are a way to access information about workflow runs, variables, runner environments, jobs, and steps. Each context is an object that contains properties, which can be strings or other objects.
You can access contexts using the expression syntax: ${{ <context> }}.
We have already seen some usage like this where we output the branch name from the github context object
echo "All the jobs completed in ${{ github.ref }} branch!" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
We can look at all the different context objects available in a workflow and we can do this by converting the objects to JSON and storing them in an environment variable on each step. Lastly, we’ll output that environment variable with a simple echo statement:
Create a new workflow with the below code:
.github/workflows/context.yaml.name: Context Information on: push: branches-ignore: main jobs: show-context: name: Show Context timeout-minutes: 5 runs-on: ubuntu-latest-internal steps: - name: Dump Event Information env: CONTEXT_ITEM: ${{ toJson(github) }} run: echo "GitHub context ${CONTEXT_ITEM}" - name: Dump Job Information env: CONTEXT_ITEM: ${{ toJson(job) }} run: echo "job context ${CONTEXT_ITEM}" - name: Dump Runner Information env: CONTEXT_ITEM: ${{ toJson(runner) }} run: echo "runner context ${CONTEXT_ITEM}" - name: Dump Step Information env: CONTEXT_ITEM: ${{ toJson(steps) }} run: echo "step context ${CONTEXT_ITEM}"Add&Commityour changes, thenPushyour branch.Go to your repository and view the
Actionstab to see the execution against your published branch.The result will be an execution of the workflow whenever any changes are pushed EXCEPT on the
mainbranch.Contextinformation is viewable in the output so that you can understand how to utilize those values in your workflows
steps context empty?In GitHub Actions, the steps context is only populated with information about the steps that have already run in the current job and have an id specified.
Let’s apply the necessary property id so we can pass data between steps:
name: Context Information
on:
push:
branches-ignore: main
jobs:
show-context:
name: Show Context
timeout-minutes: 5
runs-on: ubuntu-latest-internal
steps:
- name: Provide Some Step Outputs
id: step-outputs
run: echo "TRUE_STATEMENT=Possums are terrible." >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
- name: Dump Step Information
env:
CONTEXT_ITEM: ${{ toJson(steps) }}
run: echo "${CONTEXT_ITEM}"
The result will be that the steps context now has the data from the previous step.
You can see it’s just a JSON object and step id is the key, that is being put in the JSON object. It has to have something or else every single step that was logged here would look exactly the same and it would be ambugious.
That is why GitHub Actions enforces that if you don’t include an id, it would not log anything at all.
The context information in conjunction with conditional expressions can control the execution of various steps based on branch names, input parameters, and the success or failure of previous steps. It allows for sophisticated automation workflows that can react appropriately to different scenarios during CI/CD processes.

Global Environment Variables
Workflows allows us to define environment variables at the global level as well. These variables are then accessible to all jobs.
name: Environment Variables
on:
push:
branches: feature/global-env
env:
GLOBAL_VAR: test
jobs:
first-job:
name: A Job
timeout-minutes: 5
runs-on: ubuntu-latest-internal
steps:
- name: Output Global Variable
run: echo "${GLOBAL_VAR}"
second-job:
name: Another Job
timeout-minutes: 5
runs-on: ubuntu-latest-internal
steps:
- name: Output Global Variable
run: echo "${GLOBAL_VAR}"
The result will be a variable available across all jobs.
Workflow Defaults
Default options exist for jobs and steps within a workflow. Currently you can define the shell and working-directory
name: Using Defaults
on:
push:
branches: feature/defaults
jobs:
first-job:
name: First Job
timeout-minutes: 5
runs-on: ubuntu-latest-internal
steps:
- name: Create Source Directory
run: mkdir src
shell: bash
- name: Use Python
run: import os; print("I'm running python! Hissssss! " + os.getcwd());
shell: python
working-directory: src
- name: Use Bash
run: echo "I'm running hum-drum bash in $(pwd). Booo."
shell: bash
working-directory: src
- name: Use Bash Also
run: echo "I'm running bash also, but elsewhere in $(pwd). Booo."
shell: bash
second-job:
name: Second Job
timeout-minutes: 5
runs-on: ubuntu-latest-internal
steps:
- name: Create Source Directory
run: mkdir src
shell: bash
- name: Use Bash
run: echo "I'm running bash in $(pwd). So sad."
shell: bash
working-directory: src
The result will be an execution which utilizes bash for most of the steps within the jobs.
We could have defaults at the job level:
name: Using Defaults
on:
push:
branches: feature/defaults
jobs:
first-job:
name: First Job
timeout-minutes: 5
runs-on: ubuntu-latest-internal
defaults:
run:
shell: bash
working-directory: src
steps:
- name: Create Source Directory
run: mkdir src
working-directory: .
- name: Use Python
run: import os; print("I'm running python! Hissssss! " + os.getcwd())
shell: python
- name: Use Bash
run: echo "I'm running hum-drum bash in $(pwd). Booo."
- name: Use Bash Also
run: echo "I'm running bash also, but elsewhere in $(pwd). Booo."
working-directory: ..
second-job:
name: Second Job
timeout-minutes: 5
runs-on: ubuntu-latest-internal
steps:
- name: Create Source Directory
run: mkdir src
shell: bash
working-directory: .
- name: Use Bash
run: echo "I'm running bash in $(pwd). So sad."
shell: bash
working-directory: src
The result will be less code in your workflow, while the execution still performed the same. It used bash as the default shell and provided a default working directory of src.
We could also utilize defaults at the workflow level:
name: Job Default
on:
push:
branches: feature/defaults
defaults:
run:
shell: bash
working-directory: src
jobs:
first-job:
name: First Job
timeout-minutes: 5
runs-on: ubuntu-latest-internal
steps:
- name: Create Source Directory
run: mkdir src
working-directory: .
- name: Use Python
run: import os; print("I'm running python! Hissssss! " + os.getcwd())
shell: python
- name: Use Bash
run: echo "I'm running hum-drum bash in $(pwd). Booo."
- name: Use Bash Also
run: echo "I'm running bash also, but elsewhere in $(pwd). Booo."
working-directory: ..
second-job:
name: Second Job
timeout-minutes: 5
runs-on: ubuntu-latest-internal
steps:
- name: Create Source Directory
run: mkdir src
working-directory: .
- name: Use Bash
run: echo "I'm running bash in $(pwd). So sad."
The result will be even less code, making bash the default shell and src the working-directory for all job steps.
Dependent Jobs
Jobs by default run in parallel/asynchronously. If you need synchronous execution, you specify the dependencies via the needs keyword. The job will only execute after all jobs listed in the needs array have completed successfully. If any of the jobs in the needs list fail, the dependent job will not run.
Additionally, jobs chained in series could also share outputs. This is done through the outputs field in a job and accessed via the needs.<job_id>.outputs.<output_name> syntax.
name: Dependent Jobs
on:
push:
branches: feature/dependent
jobs:
first-job:
name: First Job (parallel)
timeout-minutes: 5
runs-on: ubuntu-latest-internal
outputs:
random-uuid: ${{ steps.uuid-gen.outputs.UUID }}
steps:
- name: Random UUID Gen
id: uuid-gen
run: echo "UUID=$(uuidgen)" >> "$GITHUB_OUTPUT"
- name: Dump Job Information
env:
CONTEXT_ITEM: ${{ toJson(job) }}
run: echo "${CONTEXT_ITEM}"
second-job:
name: Second Job (series)
timeout-minutes: 5
runs-on: ubuntu-latest-internal
needs: first-job
steps:
- name: Dump Job Information
env:
CONTEXT_ITEM: ${{ toJson(job) }}
run: echo "${CONTEXT_ITEM}"
- name: Output UUID Information
run: echo " The random UUID from the job is '${{ needs.first-job.outputs.random-uuid }}'." >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
third-job:
name: Third Job (parallel)
timeout-minutes: 5
runs-on: ubuntu-latest-internal
steps:
- name: Dump Job Information
env:
CONTEXT_ITEM: ${{ toJson(job) }}
run: echo "${CONTEXT_ITEM}"
Pull Request Triggers
GitHub Actions provides two distinct events for handling pull requests: pull_request and pull_request_target. Both can trigger workflows in response to pull request activity, but they differ significantly in their security contexts, usage scenarios, and access to repository secrets.
pull_requestEvent
Behavior:
- Triggered by events related to pull requests, such as opening a pull request, editing it, or changing its status (e.g., merging or closing).
- Runs in the context of the forked repository. This means that workflows do not have access to the secrets defined in the base repository (the repository where the pull request is being merged).
- More secure by design, preventing potentially malicious code from accessing sensitive data in the base repository.
Use Case:
You have a public repository where contributors can submit pull requests. You want to run tests to validate the code quality and ensure it meets certain standards before it can be merged. Here’s a sample workflow.yml file that uses the
pull_requestevent:name: PR Guidelines and CI on: pull_request: types: [opened, synchronize, reopened] permissions: pull-requests: write jobs: post-guidelines-comment: name: Post guidelines comment timeout-minutes: 5 runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - run: gh pr comment $PR_URL --body "$COMMENT_BODY" env: GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} PR_URL: ${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url }} COMMENT_BODY: | Thank you for your contribution! Please ensure you have followed our community guidelines and the pull request checklist: **Community Guidelines:** - Be respectful and considerate to others. - Follow the project's code of conduct. **Pull Request Checklist:** - [ ] I have read and understood the community guidelines. - [ ] My code follows the existing style of the project. - [ ] I have included tests for new features and bug fixes. - [ ] I have updated the documentation accordingly. - [ ] I have tested my changes locally. If you have any questions, feel free to reach out! test: name: CI runs-on: ubuntu-latest needs: post-guidelines-comment # Ensure this job runs after posting the comment steps: - name: Check out code uses: actions/checkout@v2 - name: Install dependencies run: npm install - name: Run tests run: npm test
- The step
post-guidelines-commentuses GitHub CLI (gh) to add a comment when a pull request is opened. To allow GitHub CLI to post a comment, we set the GITHUB_TOKEN environment variable to the value of the GITHUB_TOKEN secret, which is an installation access token, created when the workflow runs. For more information, see Automatic token authentication. We set thePR_URLenvironment variable to the URL of the newly created pull request, and we use this in theghcommand. - By default, workflows have a restricted set of permissions. Explicitly setting
pull-requests: writeallows the workflow to perform actions that modify pull requests, such as posting comments or updating labels.
pull_request_targetEvent
Behavior:
Also triggered by pull request related events, similar to pull_request. But runs in the context of the base repository. This allows workflows to have access repository secrets defined in the base repository.
Because it has access to sensitive information, it is crucial to be careful with what code is executed in this context, as it could be exploited if the pull request comes from an untrusted fork.
Use Case:
Imagine you have a repository that needs to run a deployment script or access sensitive tokens (e.g., AWS credentials) when a pull request is made. You can use the pull_request_target event to run such workflows while ensuring only trusted code runs. Here’s how you might set it up:
name: Deploy
on:
pull_request_target:
types: [opened, synchronize]
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.repo.fork == false }} # Run only for non-fork PRs
steps:
- name: Check out code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Run deployment script
env:
DEPLOY_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.DEPLOY_TOKEN }}
run: |
# Run deployment commands here
./deploy.sh
- You add a conditional check:
(if: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.repo.fork == false }})
to the deploy job. This will prevent the deployment job from executing if the pull request comes from a forked repository, thereby mitigating potential security risks.
Workflow Dispatch Triggers
Further Read
That’s all for now. Consider Intro to GitHub Actions complete, but there’s a long ways to go and lots more to learn.